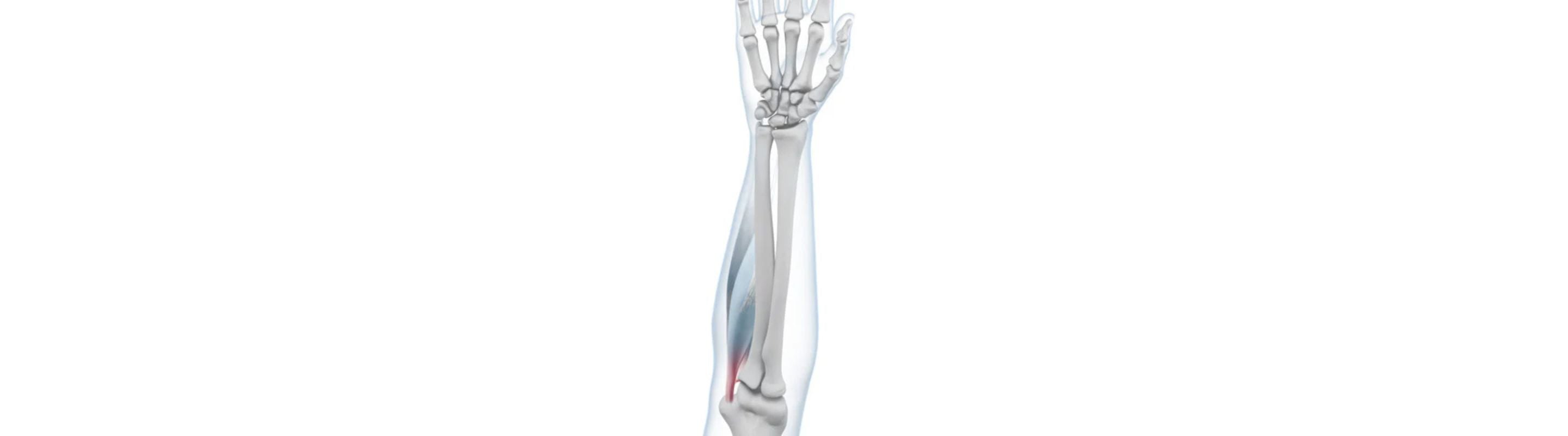
However, repeated strain or wear and tear of the muscles and tendons can lead to accumulation of these microtraumas and lead to significant pain and inflammation in the elbow. Patients suffering from this condition are diagnosed with a “Golfer’s elbow/arm” (medically referred to as Epicondylitis Humeri Ulnaris).
Causes of Golfers Elbow and Arm
Contrary to common belief, the condition isn’t exclusive to the sports domain. Golfer’s arm is a disease of the elbow joint and the muscles in it. Some of the well-known factors that can lead to developing a Golfer’s arm include:
- Repeated overstretching or overstressing of the elbow joint. This is much more common in manual labour jobs with repetitive movements like bricklayers, fencers and painters.
- Repeated stress or injury caused by sporting activities. Most typically found in athletes who are often holding a forced posture due to the nature of their sport. For example, martial arts, cricket, golf and recently e-sports athletes are commonly affected.
- Trauma in the elbow due to an accident.
- Untreated minor injuries that lead to long term build-up of micro-traumas in the elbow can lead to chronic golfer’s elbow.
Golfers Elbow and Arm Symptoms
The symptoms of golfer’s arm vary depending on the progression of the condition. Some of the more common symptoms include:
- Pain on the inside of the elbow, initially occurring only during strenuous activities. This pain is often momentary at first and usually subsides quickly. However, it is an indication of an underlying issue and should not be ignored.
Under consistent stress, the symptoms tend to get progressively worse. After progressing further, the affected muscles become very sensitive to pressure and feel warm.
- Inflammation begins and there is a tightening in the arm.
- Stiffness in the joint with any movement causing pain and rigidity.
- In chronic cases of degeneration, the entire joint can become affected. This leads to constant sharp pain.
- The mobility of the joint is severely impacted and becomes stiff, and it is common for the pain to radiate in the upper and forearm.
A prompt diagnosis is highly recommended to avoid developing chronic symptoms. An early diagnosis is the best chance at a full recovery.
Diagnosis of Golfers Elbow and Arm
A medical professional (a GP or Physio) begins with a complete patient history and physical examination of the elbow.
This provides critical information about the risk factors to the patient as well as allows for a study of the progression of the condition.
Sophisticated imaging technology like X-Rays and MRI scans can be used to get more information about the condition of the bones, muscles and tendons in the joint.
Treatment for Golfers Elbow and Arm
Treatment for golfer’s elbow/arm is mostly conservative, i.e. non-surgical. Protecting the affected tissue region and fighting inflammation are the most important aspects of an effective treatment plan. A recommended guideline would include:
Immobilisation of the Joint
It is highly recommended that the joint be relieved of all stress and be allowed to heal. Providing sufficient support and rest to the arm can itself prove to be highly effective in complete prognosis.
Rehabilitation, Physiotherapy And Occupational Therapy
Regulated physical therapy helps with targeted muscle training and is a proven effective treatment path. The physiotherapy exercises can help promote reorganization of the muscles and are the most effective option to curb the disease, and best discussed with your treatment specialist.
Regular targeted exercises can help maintain the mobility and effective functioning of the joint and is highly recommended.
Prescribed Painkillers
Painkiller such as Ibuprofen or Panadol can in some cases be used to help alleviate pain and discomfort in patients. Pain, however, is a crucial indicator of the injury. Painkillers merely mask the pain without addressing the underlying condition.
Long term use of painkillers has side-effects and can be counter-productive. These should only be used when directed by a doctor, and not for any extended periods.
Anti-Inflammation Steps
Managing inflammation is crucial to take pressure off the arm and allow for healing. There are several measures a patient can take, to seek relief from inflammation. Some of them include:
- Anti-Inflammatory medication only if prescribed by a medical practitioner.
- Electrotherapy, especially iontophoresis (the application of anti-inflammatory, pain-relieving ointments under the skin using direct current).
- Ultrasound Therapy
- Local injections of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. For example, NSAIDs have both analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects.
- Injections of Botox into the muscles to reduce the strain on the muscles.
- Application of cold blankets or cryotherapy with short-term ice packs or cold air is often effective.
- Elbow Brace And Strap
Elbow orthoses can significantly improve a patient’s quality of life. They help to reduce the pain and discomfort patients experience by taking pressure off the joint and soothing the inflamed tendons.
Wearing a Bauerfeind elbow brace like the Sports Elbow Strap or the EpiTrain helps to minimise the chances of injury by providing enhanced stability, proprioception and medical-grade compression.
This is not found in simple neoprene sleeves and braces and can be instrumental in a speedy recovery. Often protecting the elbow is enough for a complete recovery, and bracing is one of the most effective measures towards that goal.
Golfers Arm - Medical Braces Straps
EpiTrain Elbow Support
Medical braces like the Sports Elbow Strap and the EpiTrain aim to reduce the stress on the muscle at the base of the joint and helps reduce pain. The medical-grade compression helps breakdown edema (inflammatory swelling) and takes the pressure off the nerves and blood vessels in the region. The brace supports the arm in everyday movement and can lead to a significant improvement in quality of life.
The EpiTrain Elbow Support brace reduces stress on the joint and applies medical-grade compression. This promotes the breakdown of edema (inflammatory swelling) and is very comfortable for all day use. The intertwined silicon pads provide a massaging effect to alleviate the pain without limiting mobility.
The brace supports the arm in everyday movement and can lead to a significant improvement in quality of life.
The Sports Elbow Strap brace features anatomically shaped pressure pads that gently massage the arm and relieve the irritated tendons with incredible accuracy. This stimulation activates the metabolism and boosts blood circulation, thereby improving healing.
The special BOA Strap system means you can control exactly how much pressure you are putting onto the tendons at any time, meaning it can be adjusted for activities like sport, working and exercise, all while you’re still wearing it.
The breathable skin-friendly material makes it perfect for everyday use and supports healing in an ideal way.
If you are experiencing milder symptoms we would recommend the Sports Elbow Strap. Should the symptoms be more moderate to severe, we would recommend the EpiTrain. If different everyday activities result in varying degrees of discomfort, a combination of the strap and the support may work best.